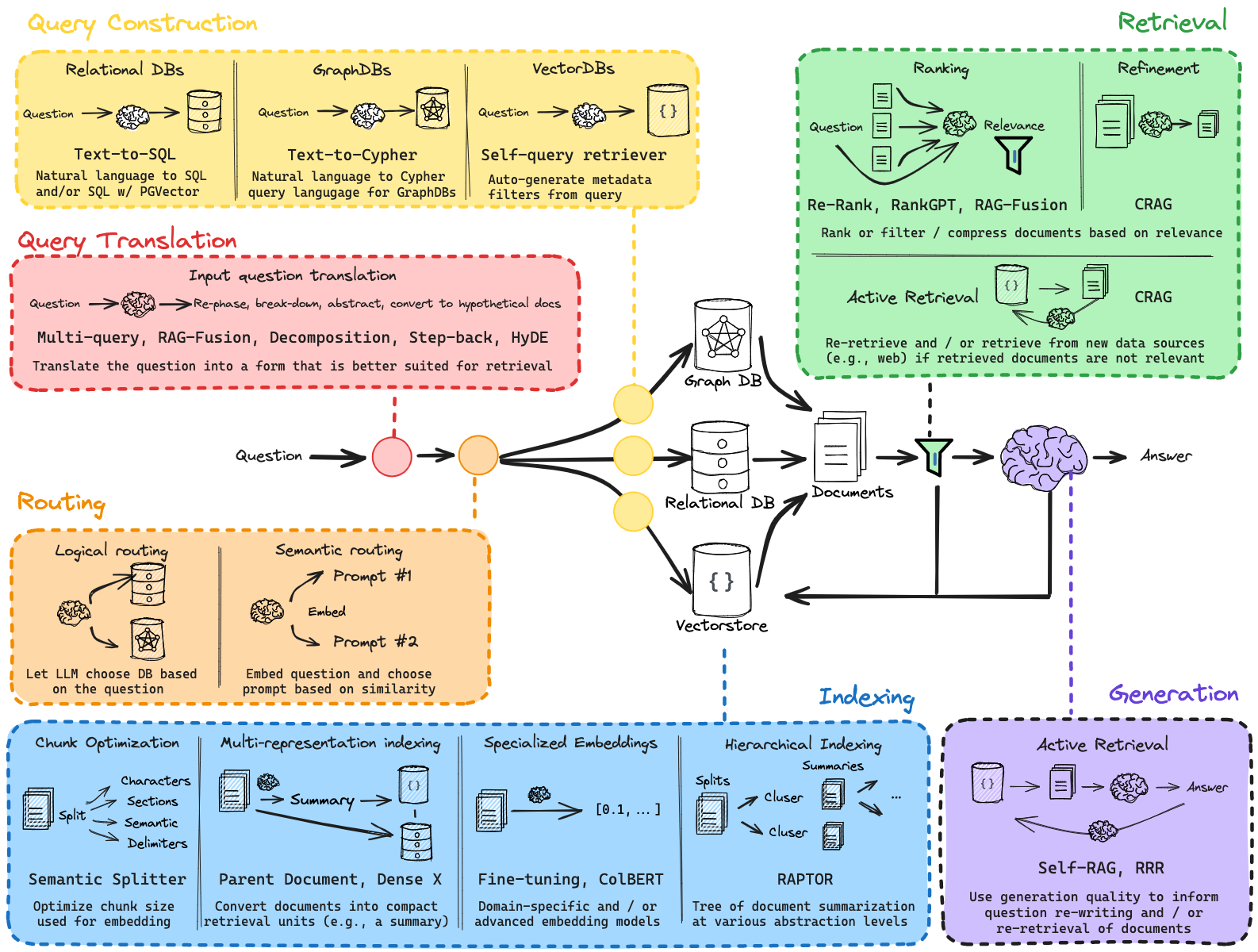
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is a framework that aids LLMs to retrieve other datasets to augment the prompt and your generate a response based off the added data source.
Breaking down the acrynpm, RAG means the following:
- Retrieval mechanism: turn your query into a vector and run a vector search from a database that has pre-encoded documents and passages
- Augmentation: Combine retrieved documents with the initial prompt to create an augmented prompt
- Answer Generation: With the new prompt, the LLM will generate a response informed by the external knowledge contained in the retrieved texts
It started with this paper: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks.
This method is particularly valuable in fields like chatbot development, where the ability to provide precise answers derived from extensive databases of knowledge is crucial.
RAG fundamentally enhances the natural language understanding and generation capabilities of models by allowing them to access and leverage a vast amount of external knowledge. The approach is built upon the synergy between two main components: a retrieval system and a generative model. The retrieval system first identifies relevant information from a knowledge base, which the generative model then uses to craft responses that are not only accurate but also rich in detail and scope.
Types of RAG
- Vector-based RAG - the most common type of RAG.
You convert text into “embeddings” and store them in a vector database.
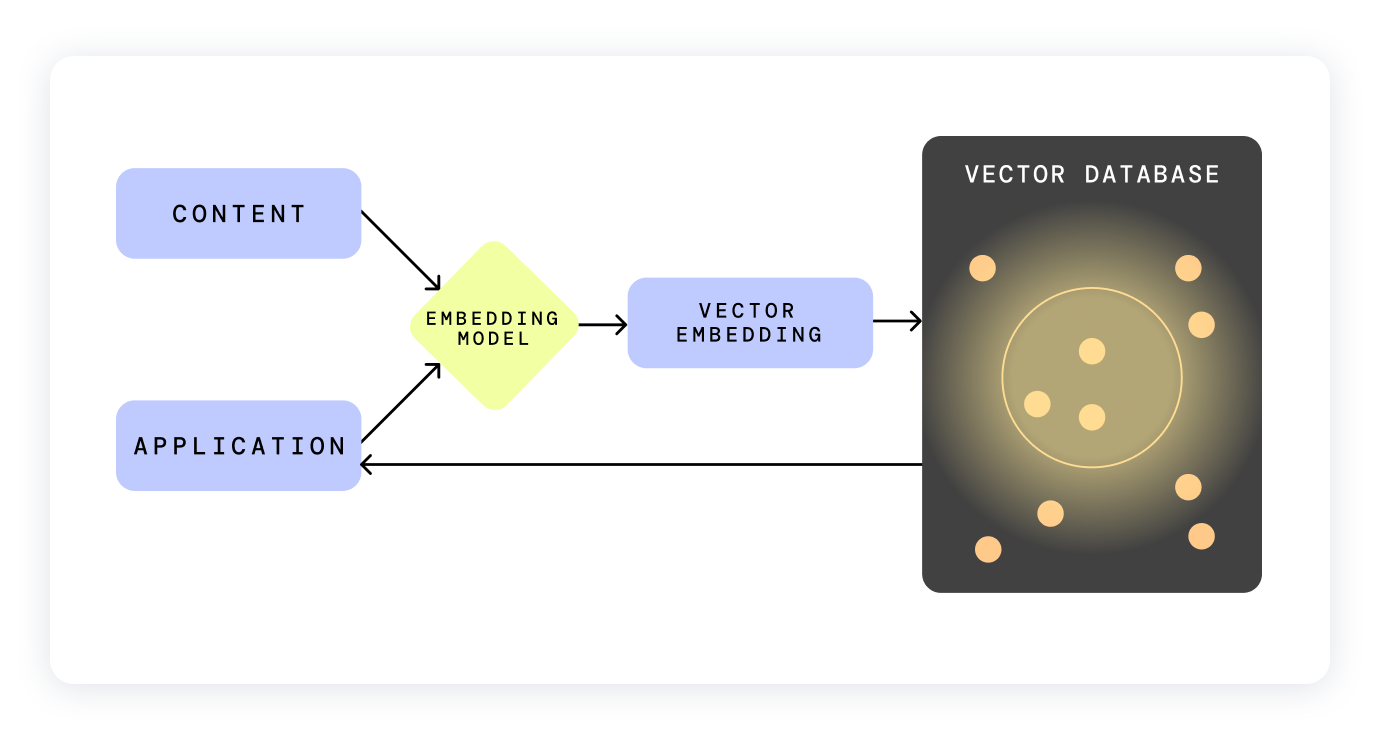
Vector databases enable search functions that are much better than typical keyword searches. If users are looking for data that has semantic similarity, a vector database can often help them find those data points, even if there isn’t a literal keyword match
— Deanna Dong, Vector databases, graph databases, and knowledge graphs - Writer
The downside is the context can be lost, especially when its relational context between data points. When chunking vectors, they use data-point similarity based on nearness. See KNN (k-nearest neighbors) and ANN (Approximate Nearest Neighbor)
- Graph-based RAG
Instead of using a vector database, you use a Graph Database. A Graph DB contains vector information where links also store data. This allows relational information from retrieval
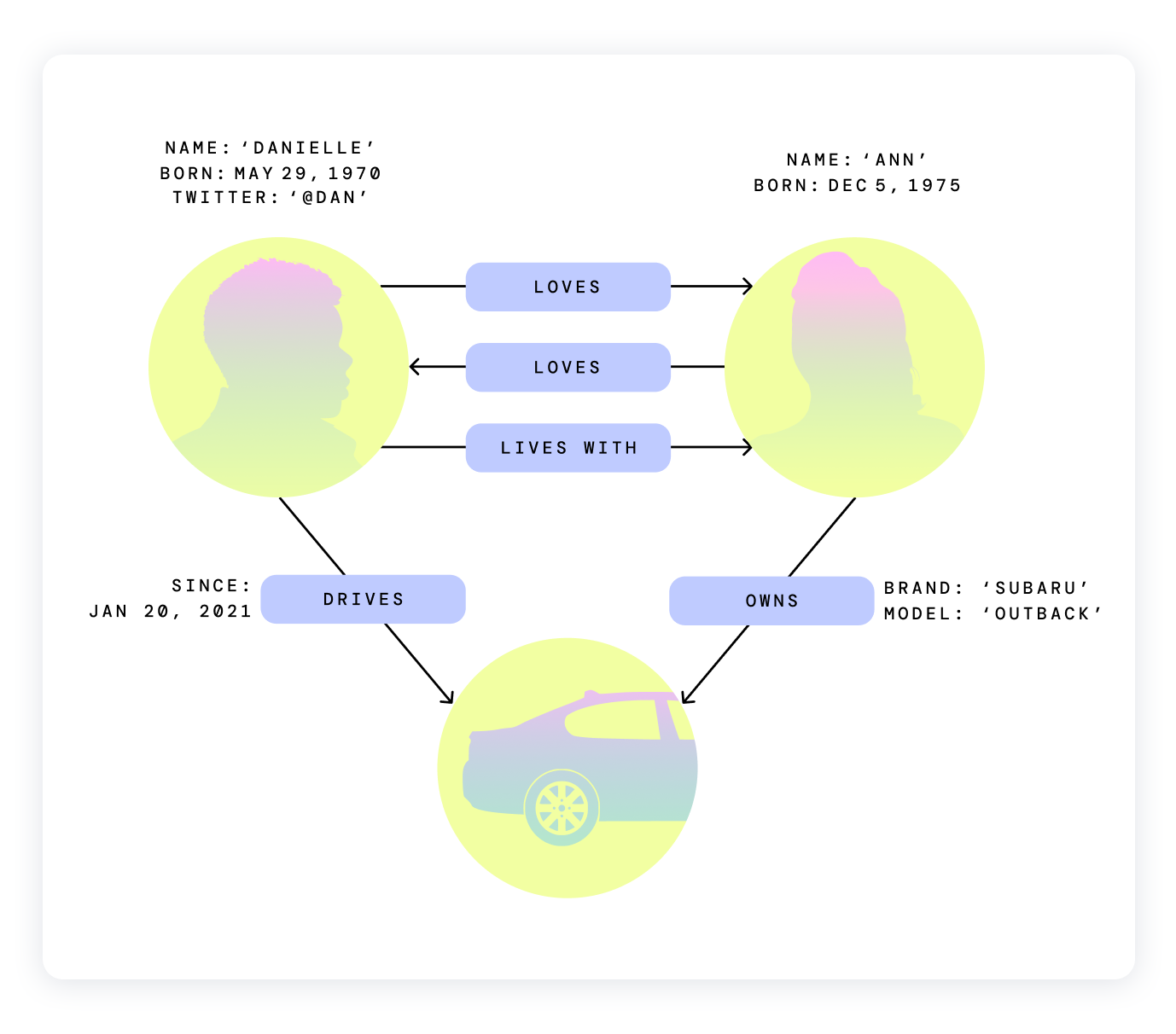
Sam Julien on X Thread - What’s graph-based RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) and why should you care?
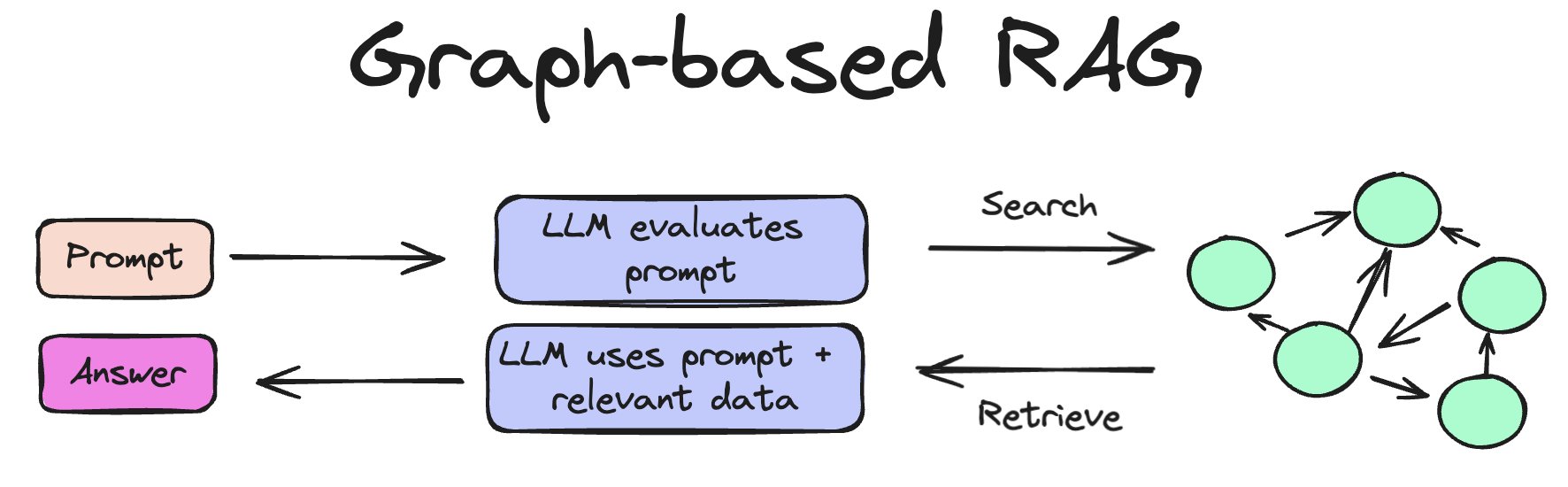
- Knowledge graphs
These outperform vector and graph databases due to their ability to preserve semantic relationships and encode structural information
Relevant sources for follow-up
- Five Reasons Enterprises Are Choosing RAG
- LangChain Github for RAG from Scratch
- Akshay 🚀 on X thread - RAGs, clearly explained
Written by Jeremy Wong and published on .